
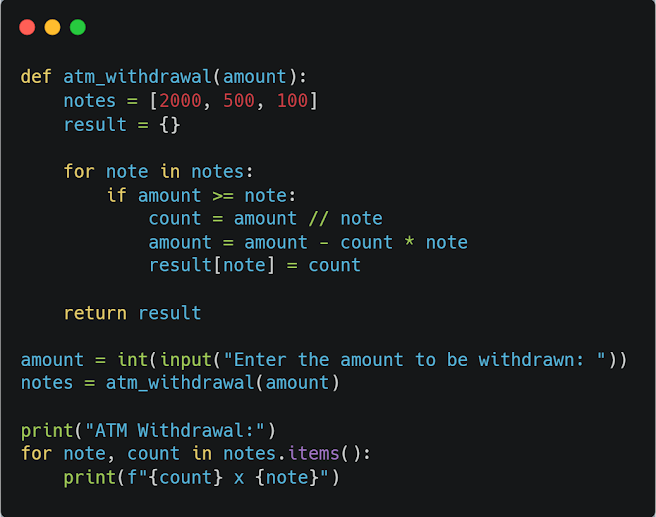
demonstrates how an ATM machine calculates and dispenses cash to customers.
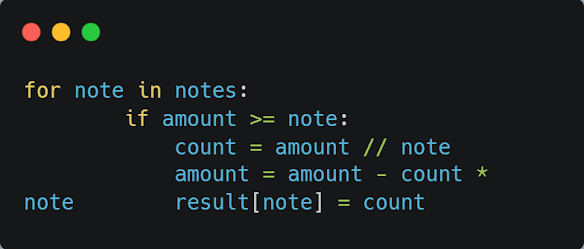
atm_withdrawal(amount), which takes an input amount representing the amount to be withdrawn. Within the function, we have a list notes containing the available denominations of notes in the ATM machine, which in this case are 2000, 500, and 100. The result dictionary is initialized as an empty dictionary, which will store the number of notes for each denomination needed to complete the withdrawal.The above code is a for loop that iterates through each denomination in the notes list. Within the loop, we use an if statement to check if the amount is greater than or equal to the current note. If it is, we use integer division // to calculate the number of notes needed, which is stored in the variable count. We then subtract count * note from amount to get the remaining amount. Finally, we add the count as the value to the current note as the key in the result dictionary.
input function to get the amount to be withdrawn from the user, which is then converted to an integer and stored in the variable amount. We then call the atm_withdrawal function and pass amount as an argument, storing the result in the notes variable.
Finally, we use a for loop to iterate through each item in the notes dictionary. Within the loop, we use string formatting to print the result in the desired format, showing the number of notes for each denomination needed to complete the withdrawal.
This is a simple implementation of an ATM withdrawal program in Python, but it demonstrates the basic logic and algorithm behind an ATM machine dispensing cash.
In conclusion, the ATM withdrawal program in Python is a simple implementation that demonstrates the logic behind an ATM machine dispensing currency. The program takes the amount to be withdrawn as input and returns the number of notes of 2000, 500 and 100 that need to be combined together in descending order to complete the withdrawn amount. This program serves as a great starting point for anyone interested in learning the basics of coding and understanding the logic behind ATM machines. I hope this post has helped you in understanding the code. Keep learning and happy coding!
If you have any questions or comments, feel free to reach out to us. We'd love to hear from you.
Stay tuned for more posts on coding and software development on the "Rohn_Codes_Life" blog. Keep coding and never stop learning!


Comments
Post a Comment